Types of Cancer Cells
Mesothelioma Cells: The Type You Have Matters
The cellular biology of cancer is complex, but understanding it can help doctors save patients’ lives.
The success of a mesothelioma treatment strategy depends on the type of cells your cancer is made of. Cell makeup matters because some treatments prove more effective against one type than another.
Also, cell type gives your doctors an indication of just how hard a punch they can throw at the disease. A knockout blow delivered with too much force can decimate not only the cancerous cells but also vitally needed healthy ones.
There are three types of mesothelioma cancer cells:
- Sarcomatoid
- Epithelioid
- Biphasic
The way you find out which cell type you have is by getting lab tests. Doctors usually do this by taking a biopsy. They then take that sample of your tumor and examine it under a microscope.
Sarcomatoid Type
Sarcomatoid is the worst type of cell, the National Cancer Institute warns. Sarcomatoids can quickly spread from the lung lining, heart lining or abdominal lining and attach to adjacent structures. These structures could include the wall of the chest or your organs themselves.
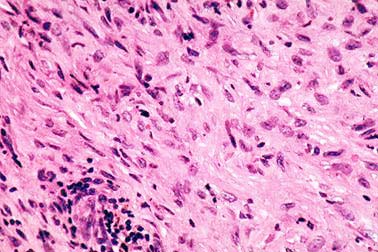
Sarcomatoid cells anchor to tissues and structures in such a way as to make treatment by surgery very difficult. Chemotherapy is only marginally more effective.
Statistically, half of the patients with sarcomatoid mesothelioma survive less than six months after diagnosis. The other half remains alive longer than six months. If you’re in this group, you may even live five or more years after diagnosis.
Epithelioid Type
Mesothelioma patients with the epithelioid cell type often have the best chances against the disease. This is, in part, because epithelioid cells grow and spread much slower than sarcomatoids.
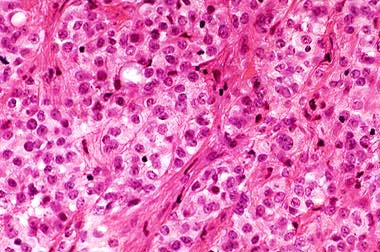
Surgery is frequently effective, especially when paired with chemotherapy, radiation therapy, or both. Aggressive cutting or dosing is usually possible.
Statistically, half of the patients with epithelial mesothelioma live less than one year after diagnosis. The other half survive longer than one year. If you’re in this group, you may even remain alive five years or more after diagnosis.
Biphasic Type
In terms of seriousness, biphasic mesothelioma cells fall somewhere between sarcomatoid and epithelioid. The reason is that a biphasic cell contains at least one sarcomatoid and at least one epithelioid cell.
How dangerous these cells are depends on the balance that exists between the sarcomatoids and epithelioids within it. Generally, the more sarcomatoids in the mix, the less effective treatment will be.
Your survival rate varies if you have biphasic-type mesothelioma cells. A higher proportion of sarcomatoids usually foretell shorter longevity, while a lower ratio may signal lengthier survival.
Incidence Rates of Mesothelioma Cells
Mesothelioma of the purely epithelioid type is the most common. The sarcomatoid type accounts for no more than one out of five cases. As many as one out of three types is of the biphasic variety, the National Cancer Institute estimates.
Of the three types, the trickiest to identify is the sarcomatoid type, since it resembles several strains of non-mesothelioma tumor cells.
Treatment Considerations
When considering treatment, remember that other factors besides cell type determine effectiveness. Therefore, it is important that you place yourself in the care of doctors who leave no aspect of this disease unexamined.
It is important for cancer patients to identify the nature of their disease as early as possible. Our patient support center’s mission is to provide you with resources and walk you through this part of the treatment process.
